Fiber optic transceivers are very common in weak current engineering. How to choose fiber optic transceivers? The fiber transceiver has failed. How to maintain it? These problems are difficult for novices, and today you will share your knowledge of fiber optic transceivers.
1. What is a fiber optic transceiver?
A fiber optic transceiver, also called a photoelectric converter, is an Ethernet transmission medium conversion unit that interchanges short-distance twisted pair electrical signals with long-distance optical signals.
Different viewing angles make people have different understandings of optical transceivers, such as single 10M, 100M optical transceivers, 10/100M adaptive optical transceivers and 1000M optical transceivers according to transmission rate; Fiber optic transceivers operating at the physical layer and fiber optic transceivers operating at the data link layer; if structured from a desktop point of view (stand-alone) fiber optic transceivers and rack-mount fiber optic transceivers; There are also two modes of multimode fiber transceivers and single mode fiber transceivers.
There are also single fiber optic transceivers and dual fiber optic transceivers, built-in power fiber optic transceivers and external power fiber optic transceivers, as well as managed fiber optic transceivers and unmanaged fiber optic transceivers. Optical transceivers break the 100-meter limitation of Ethernet cables in data transmission. By relying on high-performance switching chips and large-capacity caches, the optical transceivers provide balanced traffic and isolation conflicts while realizing non-blocking transmission switching performance. Detection of errors and other functions to ensure high security and stability during data transmission.
Second, the application of optical transceiver
In essence, the optical transceiver only completes the data conversion between different media, and can realize the connection between two switches or computers within 0--100Km, but the actual application has more expansion.
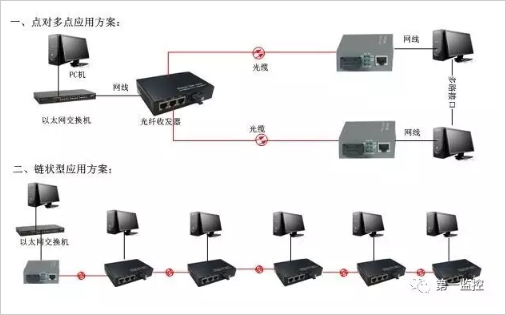
1. Implement interconnection between switches.
2. Realize the interconnection between the switch and the computer.
3. Realize the interconnection between computers.
4. Transmission relay: When the actual transmission distance exceeds the nominal transmission distance of the transceiver, especially when the actual transmission distance exceeds 100Km, it is a kind of relaying back-to-back with two transceivers when the field conditions permit. A very cost effective solution.
5. Single multimode conversion: When a single multimode fiber connection is required between networks, a multimode transceiver and a single mode transceiver can be connected back-to-back to solve the problem of single multimode fiber conversion.
6. Wavelength division multiplexing transmission: When the long-distance optical cable resources are insufficient, in order to improve the utilization rate of the optical cable and reduce the cost, the transceiver and the wavelength division multiplexer can be used together to allow two channels of information to be transmitted on the same pair of optical fibers.
Third, the use of optical transceivers
From the introduction of the opening text, we know that there are many different classifications of fiber optic transceivers, and most of the actual use is in the categories that are distinguished by fiber optic connectors: SC connector fiber optic transceivers and ST connector fiber optic transceivers.
When using a fiber optic transceiver to connect different devices, you must be aware of the different ports used.
1. Connection of fiber optic transceiver to 100BASE-TX device (switch, hub):
Confirm that the length of the twisted pair is no more than 100 meters;
Connect one end of the twisted pair cable to the RJ-45 port (Uplink port) of the fiber transceiver and the other end to the RJ-45 port (ordinary port) of the 100BASE-TX device (switch, hub).
2. Connection of the optical transceiver to the 100BASE-TX device (network card):
Confirm that the length of the twisted pair is no more than 100 meters;
Connect one end of the twisted pair cable to the RJ-45 port (100BASE-TX port) of the fiber transceiver and the other end to the RJ-45 port of the network card.
3. Connection of optical transceiver to 100BASE-FX:
Verify that the length of the fiber does not exceed the range of distances the device can provide;
One end of the fiber is connected to the SC/ST connector of the fiber transceiver, and the other end is connected to the SC/ST connector of the 100BASE-FX device.
In addition, it is necessary to add that many users use optical transceivers as long as the length of the optical fiber can be used normally within the maximum distance that single mode fiber or multimode fiber can support. In fact, this is a misunderstanding. This kind of understanding is correct only when the connected devices are full-duplex devices. When there are half-duplex devices, the transmission distance of the optical fiber has a certain limit.
Fourth, the principle of purchase
As a regional network connector device, the fiber transceiver is the main task of how to seamlessly connect the two parties. Therefore, we must consider the compatibility of its compatibility with the surrounding environment, and the stability and reliability of its own products. On the contrary: the price is lower, and it cannot be used!
1. Does it support full-duplex and half-duplex?
Some chips in the market can only use full-duplex environment at present, and can't support half-duplex. If you connect to other brands of switches (SWITCH) or hub (HUB), and it uses half-duplex mode, it will definitely cause Serious conflicts and packet loss.
2. Have you done connection testing with other fiber optic transceivers?
At present, there are more and more optical transceiver transceivers on the market. For example, if the compatibility of different brands of transceivers has not been tested beforehand, it will also result in packet loss, long transmission time, and rapid and slow.
3. Is there a safety device to prevent packet loss?
In order to reduce the cost, some manufacturers use the register data transmission mode when manufacturing the optical transceiver transceiver. The biggest disadvantage of this method is that the transmission is unstable and packet loss, and the ideal is to use the buffer circuit design. Safely avoid data loss.
4, temperature adaptability?
When the fiber optic transceiver itself is used, it will generate high heat. When the temperature is too high (generally not as large as 85 °C), does the fiber optic transceiver work normally? What is the maximum allowable operating temperature? For a device that needs long-term operation, this is worthy of our attention!
5. Is there an IEEE802.3u standard?
If the optical transceiver meets the IEEE802.3 standard, the delay time is controlled at 46 bits. If it exceeds 46 bits, the distance transmitted by the optical transceiver will be shortened! ! !
6, after sales service
In order to make the after-sales service respond promptly and early, it is recommended that the customer choose a professional company with strong strength, high technical strength and good reputation.
Five, common troubleshooting methods
1.Power light is not lit
electricity failure
2.Link light is not lit
The fault may be as follows:
(a) Check if the fiber line is open
(b) Check if the fiber line loss is too large, exceeding the receiving range of the device
(c) Check if the fiber interface is connected correctly, the local TX is connected to the remote RX, and the remote TX is connected to the local RX.
(d) Check if the fiber connector is properly inserted into the device interface, whether the jumper type matches the device interface, whether the device type matches the fiber, and whether the device transmission length matches the distance.
3. The circuit Link light is not bright
The fault may be as follows:
(a) Check if the network cable is open
(b) Check if the connection type matches: Devices such as network cards and routers use cross-lines, switches, hubs, etc., using straight-through lines.
(c) Check if the device transmission rate matches
4. Network packet loss is serious
Possible faults are as follows:
(1) The electrical port of the transceiver is connected to the network device, or the duplex mode of the interface of the two devices does not match.
(2) There is a problem with the twisted pair and the RJ-45 head.
(3) Fiber connection problem, whether the jumper is aligned with the device interface, whether the pigtail and the jumper and the coupler type match.
(4) Whether the fiber line loss exceeds the device acceptance sensitivity.
5. The fiber transceivers cannot communicate after the two ends are connected.
(1). The fiber is reversed, and the fiber connected to TX and RX is reversed.
(2). The RJ45 interface is not properly connected to the external device (note the straight through and the spliced). The fiber interface (ceramic ferrule) does not match. This fault is mainly reflected in the 100M transceiver with photoelectric mutual control function, such as APC ferrule. The transceiver connected to the transceiver of the PC ferrule will not be able to communicate normally, but the non-optical mutual control transceiver will have no effect.



